Cell No. : Cell Name
RCB5656 : HOMC-D4
update : 2024/11/11
|
| Comment | RCB5654 HOMC-A4, RCB5655 HOMC-B1, RCB5656 HOMC-D4 were derived from the same patient. |
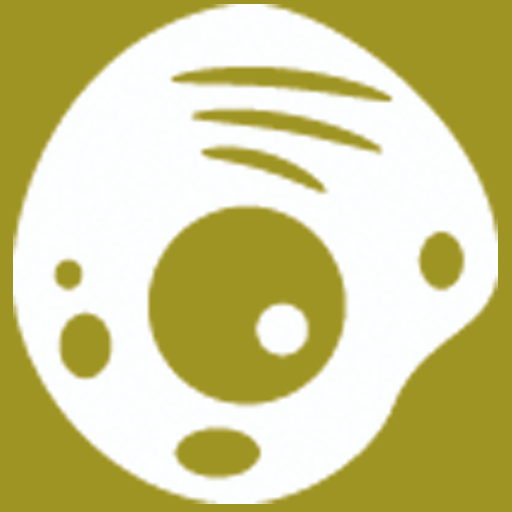
| Comment from the depositor | Human immortalized mesothelial cell line: Established from mesothelial cells derived from the greater omentum of a human male gastric cancer patient, and immortalized by transfection with human papilloma virus 16 E6/E7 gene and hTERT gene. The HOMC-D4 cell line exhibits an "intermediate" morphology by subcloning. |
| Terms and conditions | In publishing the research results obtained by use of the BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE, a citation of the following literature (Cancer Cell Int 2021 21(1):546) designated by the DEPOSITOR is requested. |
| Remarks | |
| Order Form |
Order Form(C-0005.pdf)
MTA(C-0007.pdf)
MTA(C-0007p.pdf)
|
|
Regarding MTA between user institutions and RIKEN BRC, there are two kinds of MTA, not-for-profit academic purpose (C-XXXX) and for-profit research purpose (C-XXXXp) , depending on the sort of user institutions and the purposes of use. Please use an appropriate MTA(to see). In relation to commercial use and use for patent filing, first of all Please contact RIKEN BRC (cellbank.brc@riken.jp).
|
|
|
Basic information
|
Depositor |
SEKIDO, Yoshitaka
|
| Originator |
SEKIDO, Yoshitaka
|
| Year of deposit |
2021
|
| Cloning (depositor) |
Yes
|
| Animal |
_human
< Mammals
|
| Genus |
Homo
|
| Species |
sapiens
|
| Race |
Japanese
|
| Gender |
Male
|
| Age at sampling |
51 years
|
| Tissue |
greater omentum
|
| Disease name |
gastric cancer
|
| Classification |
cancer
|
| Recombinant |
recombinant
|
| Exogene |
human papillomavirus (pCLXN-16E6E7), human TERT (pCMSVpuro-hTERT)
|
| Selection |
G418 (200 microgram/ml), puromycin (1 microgram/ml)
|
| Recombinant virus |
No
|
|
Lifespan |
infinite
|
| Morphology |
intermediate (epithelioid and sarcomatoid)
|
| Tumorigenesis |
No
|
|
| |
deposit info |
lot info |
|
Medium |
Medium List |
|
Culture type |
Adherent cells
|
Adherent cells
|
| Culture medium |
RPM1640 + 10% FBS
|
RPMI1640 + 10% FBS
|
| Antibiotics |
1% antimicrobial
|
Free
|
|
Passage method |
0.25% Trypsin EDTA
|
0.25% Trypsin + (0.02% EDTA or 0.04% EDTA)
|
Culture information
|
Passage ratio |
1/4 - 1/10
|
1 : 4-10 split
|
| SC frequency |
Subculture : 2 times/week
|
Subculture : 2 times/week
|
| Temperature |
37
℃
|
37
℃
|
| CO2 concentration |
5
%
|
5
%
|
| Freeze medium |
CELLBANKER
|
CELLBANKER 1
|
| Freezing method |
|
Slow freezing
|
| Mycoplasma/Acholeplasma |
|
(-)
|
| Animal PCR |
|
OK
|
| Virus (EBV) |
|
(-)
|
| STR(human) |
|
OK
|
| Images |
deposit info | lot info |
|
|
|
| Reference information |
Reference |
5
|
| User's Publication |
0
|
| Reference |
|
20921
Koya Suzuki, Masaki Tange, Ryota Yamagishi, Hiroyuki Hanada, Satomi Mukai, Tatsuhiro Sato, Takeshi Tanaka, Tomohiro Akashi, Kenji Kadomatsu, Tohru Maeda, Takashi Miida, Ichiro Takeuchi, Hiroshi Murakami, Yoshitaka Sekido & Yuko Murakami-Tonami
SMG6 regulates DNA damage and cell survival in Hippo pathway kinase LATS2-inactivated malignant mesothelioma
Cell Death Discovery
2022
8, Article number: 446
PubMed ID: 36335095
DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01232-w
|
|
16028
Sato T, Nakanishi H, Akao K, Okuda M, Mukai S, Kiyono T, Sekido Y.
Three newly established immortalized mesothelial cell lines exhibit morphological phenotypes corresponding to malignant mesothelioma epithelioid, intermediate, and sarcomatoid types, respectively
Cancer Cell Int
2021
21(1):546
PubMed ID: 34663305
DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-02248-5
|
|
16027
Matsushita A, Sato T, Mukai S, Fujishita T, Mishiro-Sato E, Okuda M, Aoki M, Hasegawa Y, Sekido Y.
TAZ activation by Hippo pathway dysregulation induces cytokine gene expression and promotes mesothelial cell transformation
Oncogene
2018
38(11):1966-1978
PubMed ID: 30401981
DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0417-7
|
|
16026
Kakiuchi T, Takahara T, Kasugai Y, Arita K, Yoshida N, Karube K, Suguro M, Matsuo K, Nakanishi H, Kiyono T, Nakamura S, Osada H, Sekido Y, Seto M, Tsuzuki S.
Modeling mesothelioma utilizing human mesothelial cells reveals involvement of phospholipase-C beta 4 in YAP-active mesothelioma cell proliferation
Carcinogenesis
2016
37(11):1098-1109
PubMed ID: 27559111
DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgw084
|
|
17320
Kyo S, Nakamura M, Kiyono T, Maida Y, Kanaya T, Tanaka M, Yatabe N, Inoue M.
Successful immortalization of endometrial glandular cells with normal structural and functional characteristics
Am J Pathol
2003
163(6):2259-69
PubMed ID: 14633600
DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63583-3
|
 CELL BANK Website
CELL BANK Website
 Back
Back
 Top
Top
 Top
Top
 Back
Back