CELL BANK Website
CELL BANK Website
 Back
Back
|
Cell No. : Cell Name
RCB3707 : Atg7 -/- MEFs update : 2025/01/16 |
||||
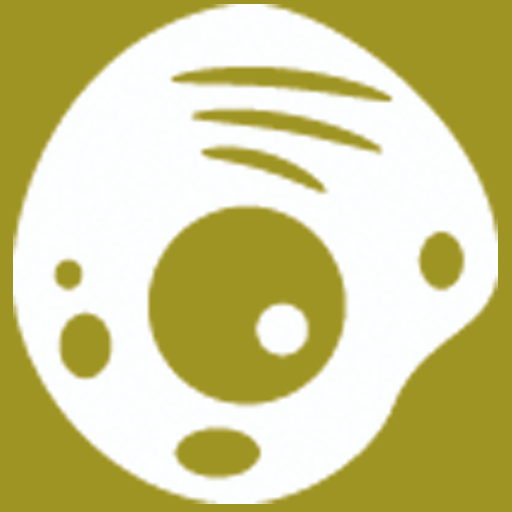
| Comment | Mouse embryonic fibroblasts derived from Atg-deficient mouse (C57BL/6). | |||
| Comment from the depositor | ||||
| Terms and conditions | 1) The RECIPIENT of BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE shall obtain a prior written consent on use of it from the approver. 2) The RECIPIENT must contact the DEVELOPER in case of application for any patents or commercial use with the results from the use of BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE. 3) In publishing research results obtained by the use of the BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE, a citation of the literature ref. (J Cell Biol 2005;169:425-434) designated by the DEPOSITOR is required. 4) In publishing the research results to be obtained by use of the BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE, an acknowledgment to the DEPOSITOR is requested. 5) The RECIPIENT of BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE who belongs to a profit organization must obtain a prior written consent on use of it from the DEPOSITOR. | |||
| Remarks | ||||
| approver's address |
×
|
|||
| Order Form | Order Form(C-0005.pdf) Approval Form(C-0006.pdf) MTA(C-0007.pdf) MTA(C-0007p.pdf) | |||
| Regarding MTA between user institutions and RIKEN BRC, there are two kinds of MTA, not-for-profit academic purpose (C-XXXX) and for-profit research purpose (C-XXXXp) , depending on the sort of user institutions and the purposes of use. Please use an appropriate MTA(to see). In relation to commercial use and use for patent filing, first of all Please contact RIKEN BRC (cellbank.brc@riken.jp). | ||||
| Basic information | Depositor | Komatsu, Masaaki | ||
| Originator | Komatsu, Masaaki | |||
| Year of deposit | 2011 | |||
| Animal | _mouse < Mammals | |||
| Strain name | C57BL/6 | |||
| Gender | Unknown | |||
| Age at sampling | embryo | |||
| Tissue | embryo/fetus, whole | |||
| Classification | mutant | |||
| Recombinant | recombinant | |||
| Exogene | SV40 large T, pMESVts, Neomycin resistance gene | Lifespan | infinite | |
| Morphology | fibroblast-like | |||
| Cellosaurus(Expasy) | CVCL_VQ61 | |||
| Medium | Medium List | Culture type | Adherent cells | |
| Culture medium | DMEM (high glucose, without Sodium Pyruvate) + 10% FBS | |||
| Antibiotics | Free | Passage method | 0.25% Trypsin | Culture information | Passage ratio | 1 : 8 split |
| SC frequency | Subculture : 2 times/week | |||
| Temperature | 33 ℃ | |||
| CO2 concentration | 5 % | |||
| Freeze medium | Medium + 10% DMSO | |||
| Freezing method | Slow freezing | |||
| Mycoplasma/Acholeplasma | (-) | |||
| Animal PCR | OK | |||
| SSLP(mouse) | OK | |||
| Images | ||||
|
|
|
|||
| Reference information | Reference | 1 | ||
| User's Publication | 5 | |||
 Top
Top
 Top
Top
 Back
Back